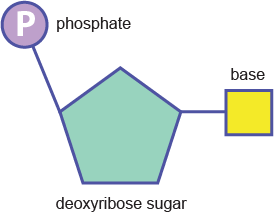
41 three parts of a nucleotide
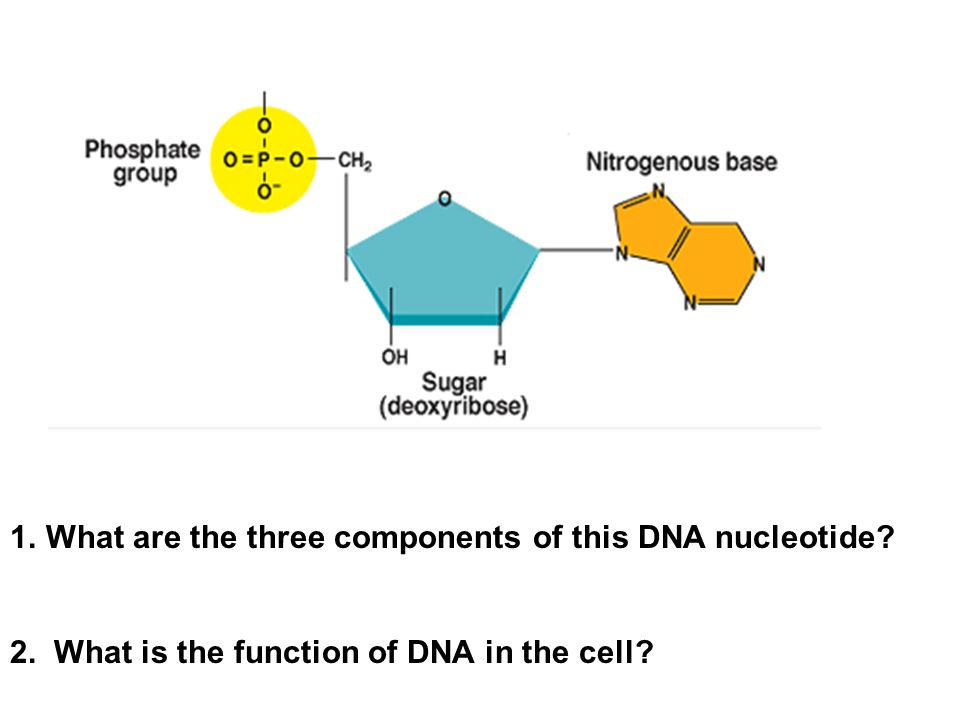
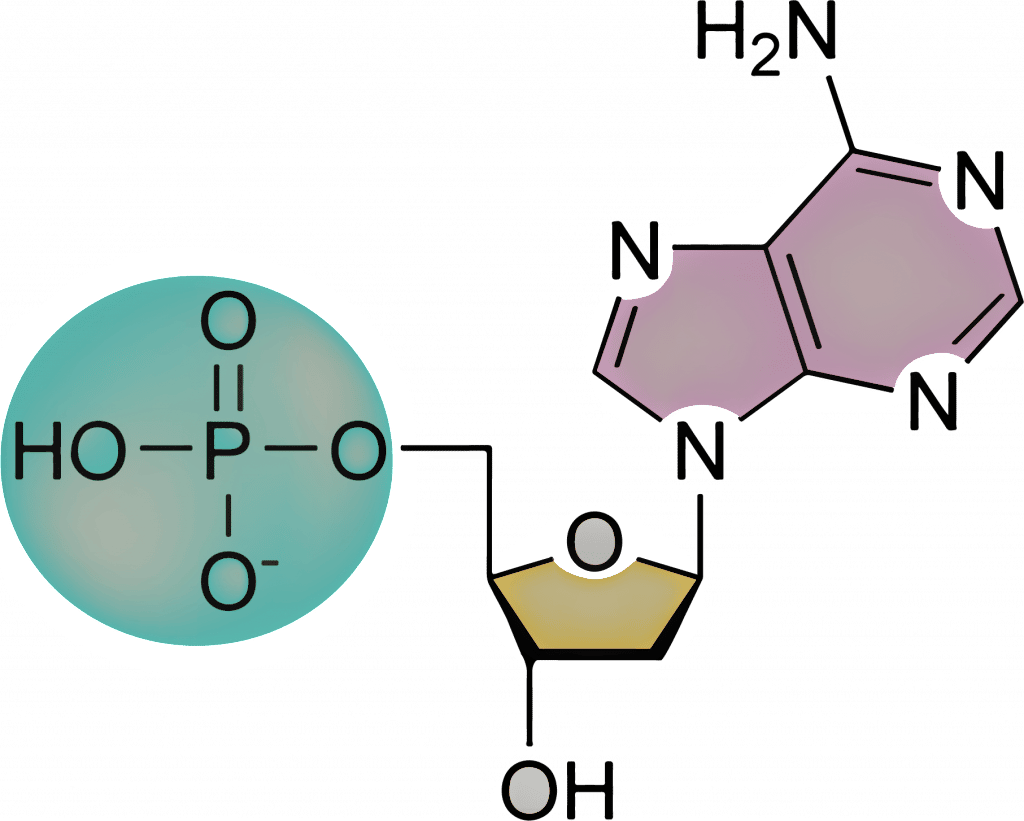
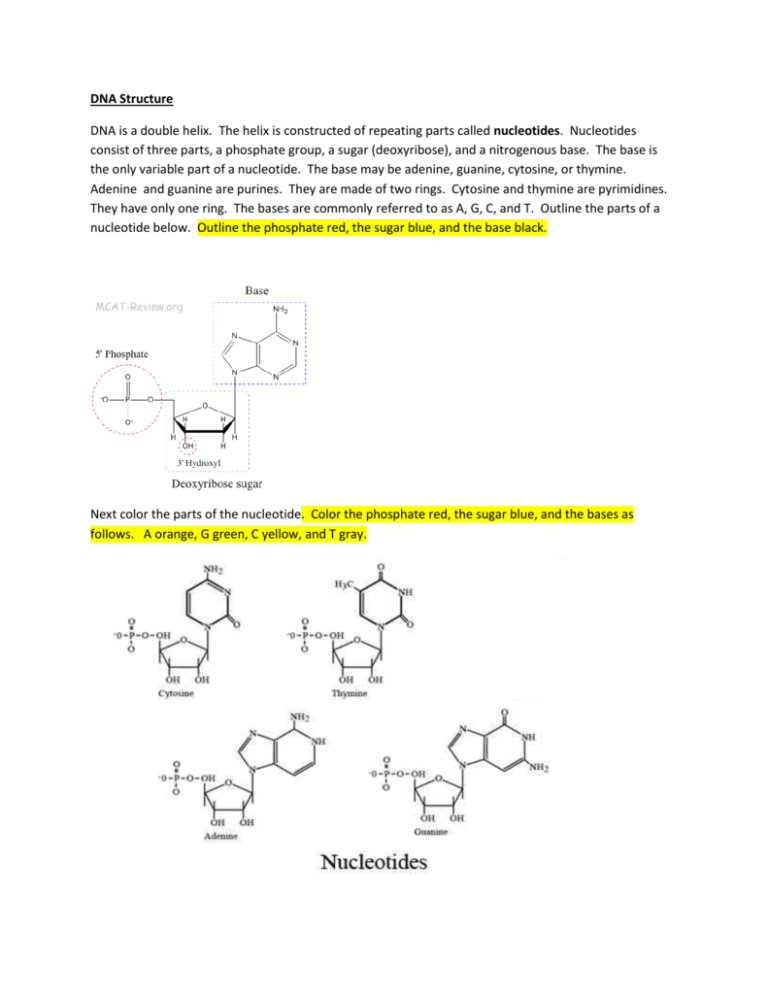
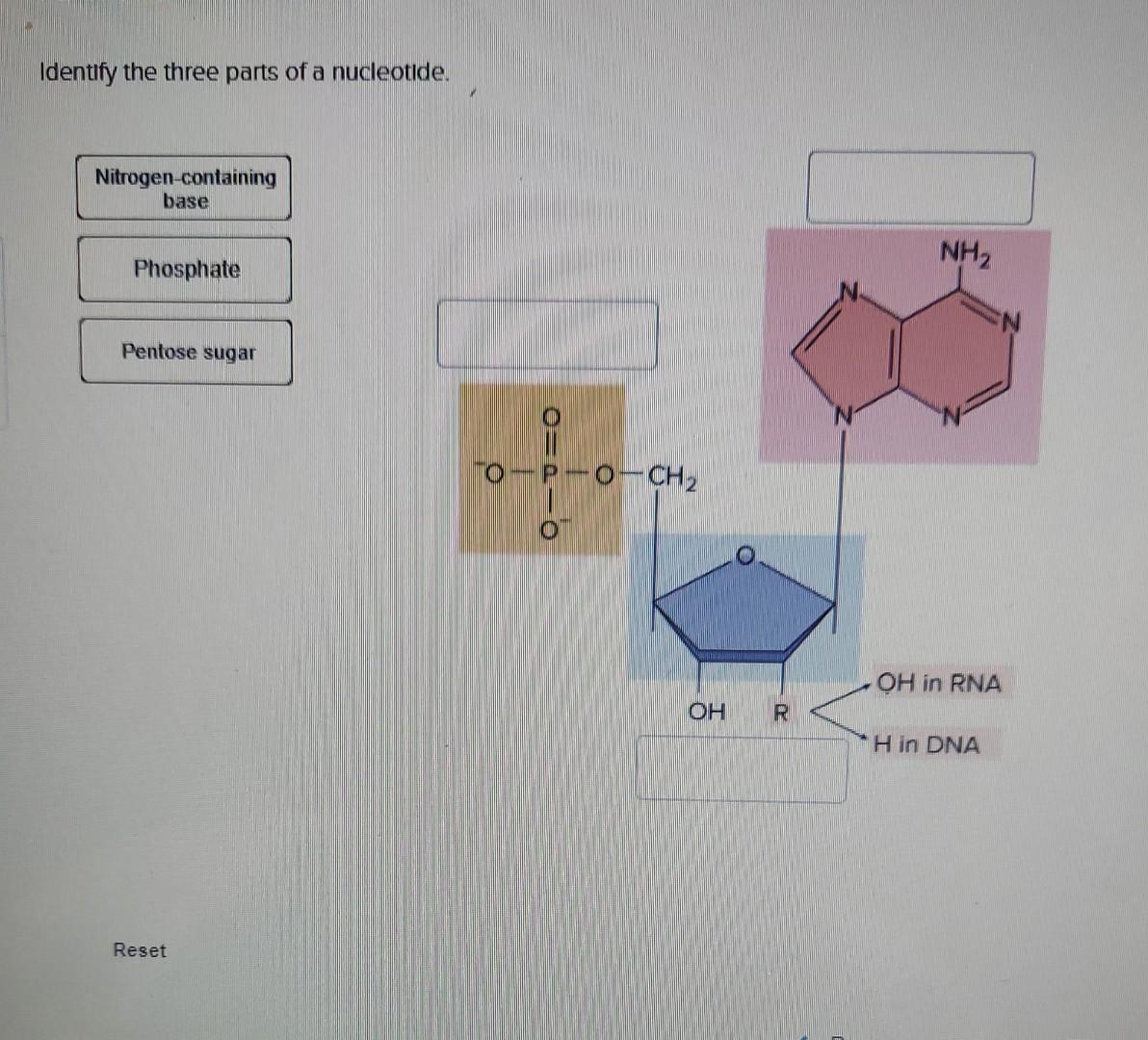
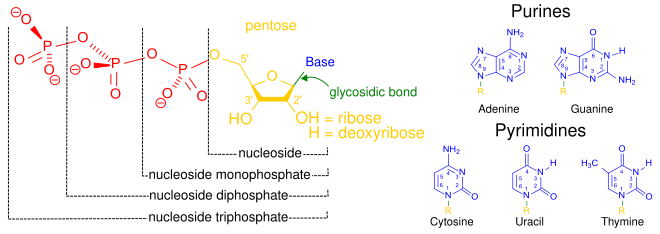
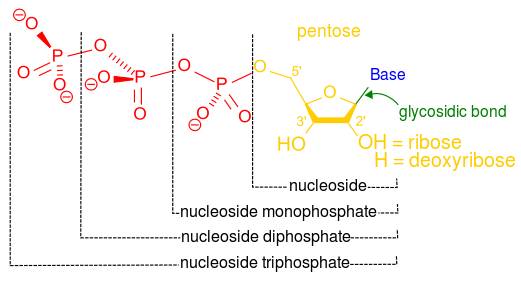
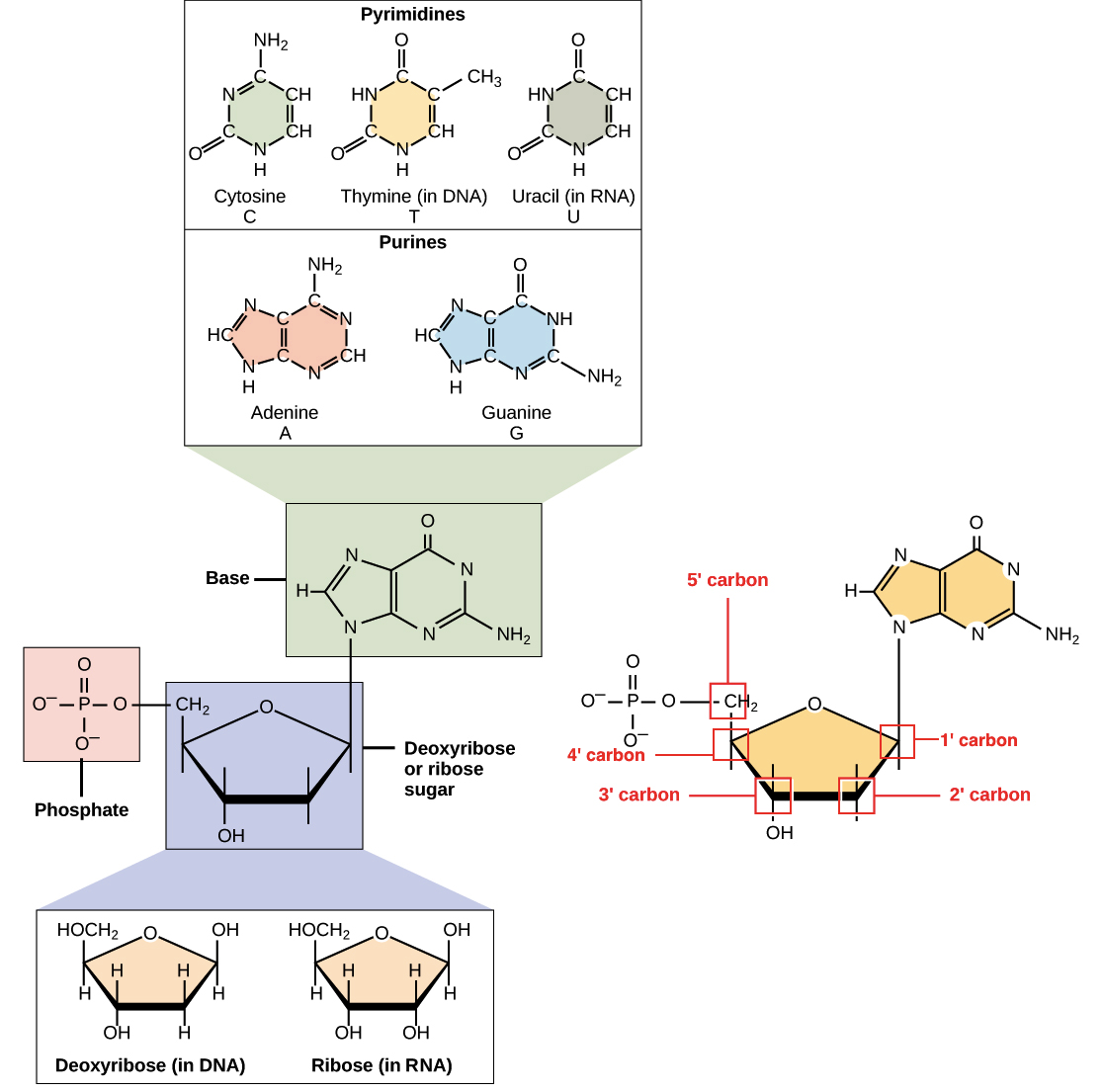
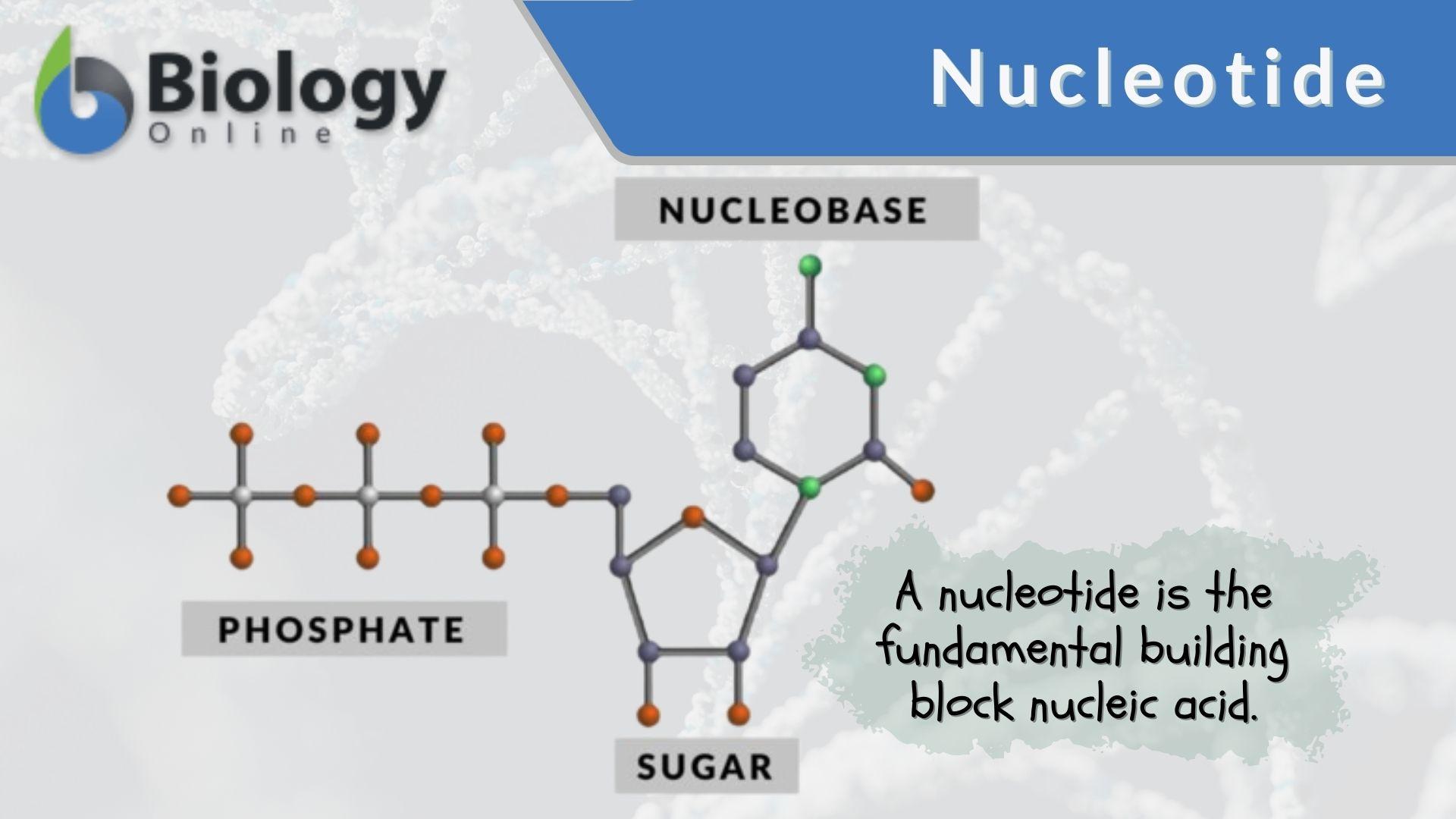
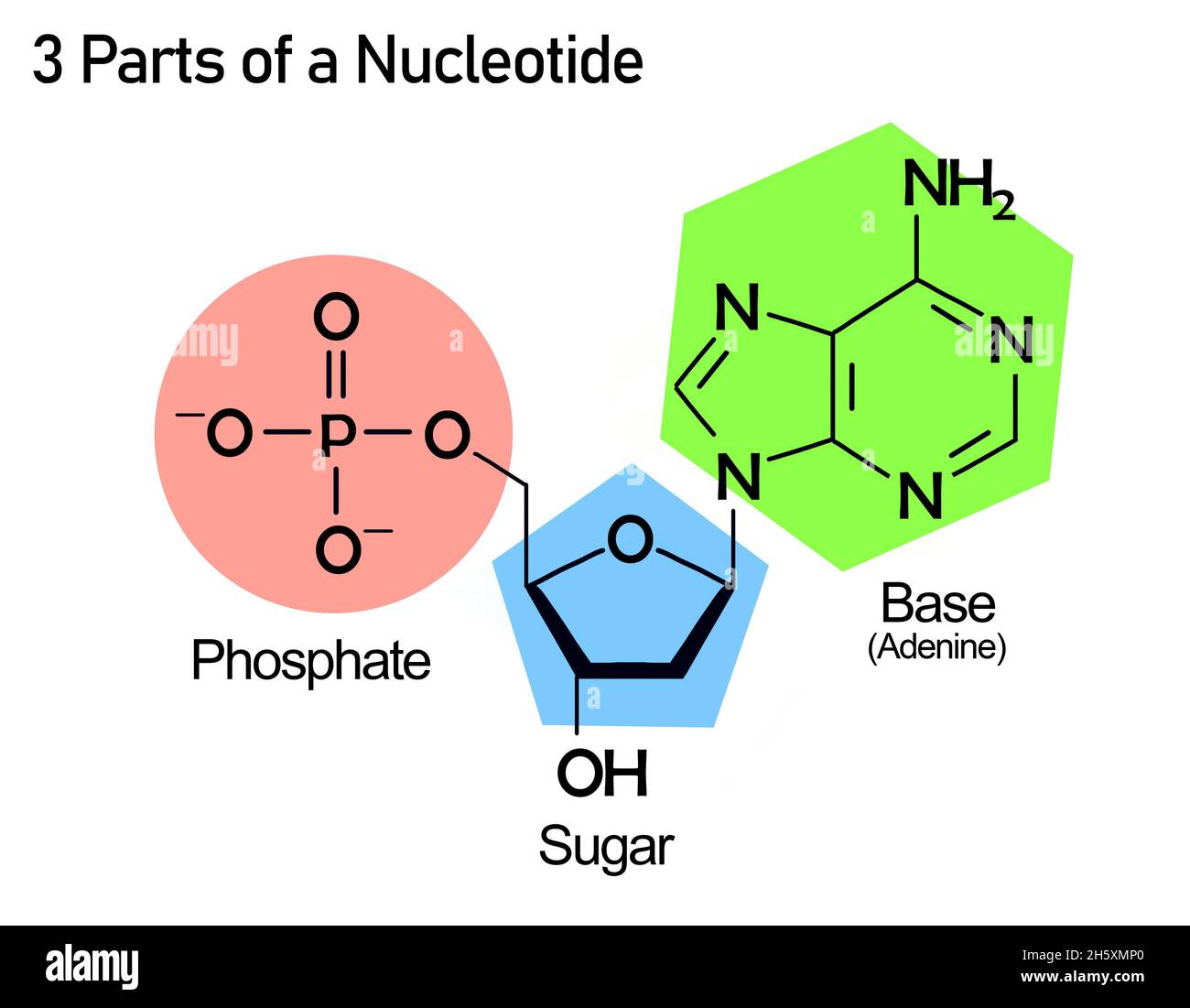
DNA Is a Structure That Encodes Biological Information At the most basic level, all DNA is composed of a series of smaller molecules called nucleotides.In turn, each nucleotide is itself made up of three primary components: a nitrogen-containing ... What are the Three Main Parts of a Nucleotide? - BYJU'S There are a total of five bases found in the DNA and RNA world, namely - Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), Thymine (T) and Uracil (U). A, T, C and G are found in DNA molecules whereas the uracil base is found in RNA molecules in place of the thymine. Phosphate Group
Nucleotide - Genome A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). In RNA, the base uracil (U) takes the place of thymine.

Three parts of a nucleotide
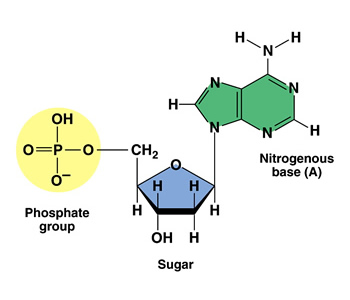
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? - Science Notes and Projects The three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA (2′-deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA and RNA code genetic information, transport energy throughout cells, and serve as cell signaling molecules. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Flashcards | Quizlet Nucleotide. basic unit. surgery in DNA. deoxylibonuelic. hydrogen bonds. hold DNA together. covalent bond is. sharing of electrons. ionic is the attraction between. Nucleic Acids - Function, Examples, and Monomers - ThoughtCo OpenStax/Wikimedia Commons/CC BY-SA 3.0. Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotide monomers linked together. Nucleotides have three parts: A Nitrogenous Base; A Five-Carbon (Pentose) Sugar; A Phosphate Group; Nitrogenous bases include purine molecules (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidine molecules (cytosine, thymine, and uracil.) In DNA, the ...
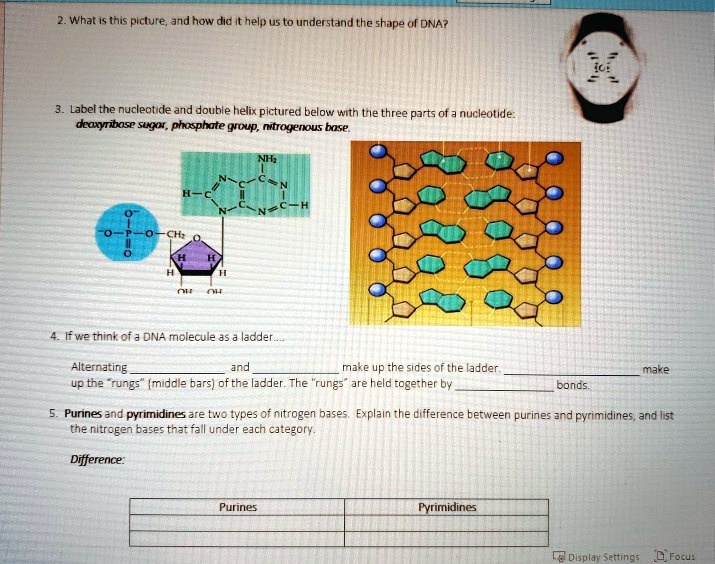
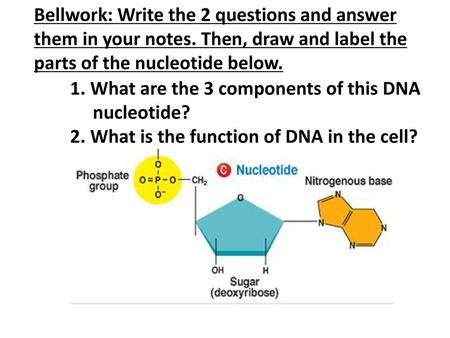
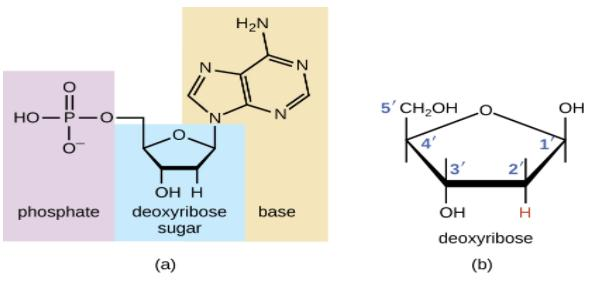
Three parts of a nucleotide. Learn about the three parts of the nucleotide - base, sugar, and phosphate - along with a descriptive image in this solution by a Bartleby expert. Skip to main content bartleby learn write plus study resources expand_more StudyResources We Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. RNA contains uracil, instead of thymine. A nucleotide within a chain makes up the genetic material of all known living things. What Are The Three Parts Of A Nucleotide | Jacks Of Science Each nucleotide is composed of three parts: a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogen-containing base. The sugar molecule can be either ribose or deoxyribose, and the phosphate group is bonded to the sugar via a phosphodiester bond. The nitrogen-containing base is attached to the sugar via a nitrogenous base pair. What is a phosphate group? 9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology | OpenStax Now let's consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base ( Figure 9.3 ). There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA.
DNA structure and replication review (article) | Khan Academy In DNA, each nucleotide is made up of three parts: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. DNA uses four kinds of nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G) cytosine (C), and thymine (T). ... DNA is synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction, while in lagging strand, DNA is synthesized in the 3' to 5 ... Nucleotide - Wikipedia A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase (the two of which together are called a nucleoside), and one phosphate group.With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleoside monophosphate", "nucleoside diphosphate" or "nucleoside triphosphate", depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate group. Nucleotides: Definition, Component & Structure | StudySmarter 3 parts of a Nucleotide. A nucleotide has three major components: a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Let's look into each of these and see how they interact to form a nucleotide. Nitrogenous base. Nitrogenous bases are organic molecules containing one or two rings with nitrogen atoms. Nucleic acids (article) | Khan Academy Each nucleotide is made up of three parts: a nitrogen-containing ring structure called a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and at least one phosphate group. ... meaning that the nucleotide at the 5' end comes first and the nucleotide at the 3' end comes last. As new nucleotides are added to a strand of DNA or RNA, the strand grows at its 3 ...
2.6: DNA and RNA Flashcards | Quizlet A nucleotide has three component parts: 1. a nitrogenous base 2. A 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) 3. A phosphate group Identify and label carbons by number (for example, C1, C2, C3) on a nucleotide drawing. Understanding: The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides. What are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io Nucleotides are made up of 3 parts. The first is a distinct nitrogenous base, which is adenine, cytosine, guanine or thymine. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil. These nitrogenous bases are either purines or pyrimidines. Base pairs are formed when adenine forms a hydrogen bond with thymine, or cytosine forms a hydrogen bond with guanine. 3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected - ThoughtCo Nucleotides in DNA and RNA Both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Nitrogenous Base Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. DNA function & structure (with diagram) (article) | Khan Academy A nucleotide contains adenine T nucleotide contains thymine G nucleotide contains guanine C nucleotide contains cytosine All four of these nucleobases are relatively complex molecules, with the unifying feature that they all tend to have multiple nitrogen atoms in their structures.
16.6: Nucleic Acids- Parts, Structure, and Function Adenine and guanine are the major purines found in nucleic acids (Figure 16.6. 1 ). Figure 16.6. 1 The Nntrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA. The formation of a bond between C1′ of the pentose sugar and N1 of the pyrimidine base or N9 of the purine base joins the pentose sugar to the nitrogenous base. In the formation of this bond, a ...
Nucleic Acids - Function, Examples, and Monomers - ThoughtCo OpenStax/Wikimedia Commons/CC BY-SA 3.0. Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotide monomers linked together. Nucleotides have three parts: A Nitrogenous Base; A Five-Carbon (Pentose) Sugar; A Phosphate Group; Nitrogenous bases include purine molecules (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidine molecules (cytosine, thymine, and uracil.) In DNA, the ...
What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Flashcards | Quizlet Nucleotide. basic unit. surgery in DNA. deoxylibonuelic. hydrogen bonds. hold DNA together. covalent bond is. sharing of electrons. ionic is the attraction between.
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? - Science Notes and Projects The three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA (2′-deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). DNA and RNA code genetic information, transport energy throughout cells, and serve as cell signaling molecules.




![Solved Question 2 [3 marks]: As mentioned above, each | Chegg.com](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/232/23252d7f-6449-44ca-bd85-b584d9c56540/php92BcUD.png)














.jpg)


Komentar
Posting Komentar